¿Qué es la clonación?
Es una reproducción asexuada que origina individuos genéticamente idénticos. La hay de dos tipos; en la natural el hombre no interviene (regeneración de células idénticas a la original mediante el proceso de mitosis), mientras que en la artificial, recientemente descubierta, el hombre participa activamente.
La clonación humana, una
perspectiva general
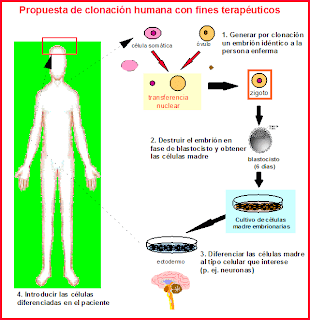
Ésta es la manera de ser clonados. Los científicos obtendrían su ADN de una célula epidérmica y lo colocarían en el óvulo de una mujer cuyo ADN fue extraído. Una chispa de electricidad dividiría el óvulo y, después de algunos días, obtendríamos un embrión igual al otro. .jpg) Se ha hablado mucho en prensa sobre la clonación humana. En la
realidad, la mayoría de los científicos no está interesada en producir clones
humanos. Lo que los científicos pretenden hacer es producir células humanas
clonadas que puedan utilizarse para curar algunas enfermedades. Se ha hablado mucho en prensa sobre la clonación humana. En la
realidad, la mayoría de los científicos no está interesada en producir clones
humanos. Lo que los científicos pretenden hacer es producir células humanas
clonadas que puedan utilizarse para curar algunas enfermedades.
Así es cómo podría funcionar: imagine que padece de una
enfermedad que le está destruyendo partes de su cerebro lentamente. Los
tratamientos actuales apenas reducen los síntomas mientras que la enfermedad
continúa provocando lesiones en su cerebro. La clonación le ofrece una
esperanza de cura.
Los científicos producirían un embrión clonado utilizando el
ADN de sus células epidérmicas. A continuación, retirarían las células madre de
este embrión, transformándolas en células cerebrales y por último las
transplantarían a su cerebro.
|
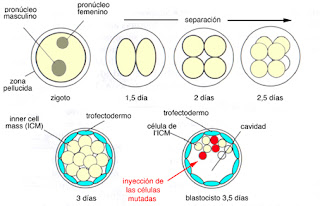 La clonación molecular :consiste en el aislamiento de una
secuencia de ADN de una célula y así obtener copias indefinidas de ésta. Se
utiliza en laboratorios para obtener por ejemplo grandes cantidades de una
proteína específica. Esta clonación cumple con cuatro etapas; fragmentación,
ligación, transfección y selección. Luego de esto, las células clonadas reciben
un cultivo especial
La clonación molecular :consiste en el aislamiento de una
secuencia de ADN de una célula y así obtener copias indefinidas de ésta. Se
utiliza en laboratorios para obtener por ejemplo grandes cantidades de una
proteína específica. Esta clonación cumple con cuatro etapas; fragmentación,
ligación, transfección y selección. Luego de esto, las células clonadas reciben
un cultivo especialLa clonación celular: que consiste en crear una población celular a partir de una sola célula. El proceso se hace utilizando la técnica in Vitro.
La clonación terapéutica: se utiliza para la investigación celular. Consiste en la producción de embriones humanos, pero no con el objetivo de crear personas, sino para investigaciones sobre el desarrollo humano. Buscan prevenir enfermedades o remediar algunas, como el cáncer, alzheimer, entre otras. En la actualidad ha sido muy trascendente, pues los científicos reemplazan células dañinas por las clonadas y así acabar por completo algún tipo de patología.
 La
clonación de organismos: consiste en un procedimiento de crear un individuo genéticamente
idéntico a otro. Este tipo de clonación es aplicable a plantas, semillas,
árboles frutales, etc.
La
clonación de organismos: consiste en un procedimiento de crear un individuo genéticamente
idéntico a otro. Este tipo de clonación es aplicable a plantas, semillas,
árboles frutales, etc.Dentro de la clonación de organismos, está la practicada en animales. El proceso consiste en la extracción del núcleo de una célula adulta llamada célula somática a un óvulo al que se le extrajo su núcleo previamente. Luego el óvulo con el núcleo de la célula somática es insertado en un útero.
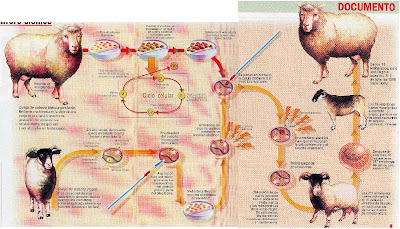 El
primero en acercarse a este tipo de clonación fue John Gurdon en El procedimiento del
experimento de la oveja Dolly fue el siguiente. Se extrajo el núcleo de una
célula de ubre de una oveja. De otra se toma un óvulo no fecundado y se le
inserta el núcleo de la célula de ubre.
El
primero en acercarse a este tipo de clonación fue John Gurdon en El procedimiento del
experimento de la oveja Dolly fue el siguiente. Se extrajo el núcleo de una
célula de ubre de una oveja. De otra se toma un óvulo no fecundado y se le
inserta el núcleo de la célula de ubre. El óvulo es sometido a una descarga eléctrica para que se fecunde. Ya formado el embrión, éste se inserta en el útero de una tercera oveja se desarrolla y nace Dolly, idéntica a la oveja que se le extrajo la célula de ubre.
Tras este experimento,
los científicos se cuestionaron sobre la clonación humana, pero en este terreno
entra fuertemente la bioética y la religión. Éstos últimos sostienen que un ser
humano clonado carecería de individualidad, no tendría padres, sería una
especie de máquina. Aspectos que atentan contra la dignidad y derechos del
hombre. Un tema polémico pero de gran interés científico.
What is cloning?
Is asexual reproduction that causes genetically identical individuals. The there are two types, in the natural man does not intervene (regeneration of cells identical to the original through the process of mitosis), whereas in the artificial recently discovered active man.
.jpg) Cloning
means producing a genetically identical copy of an
individual.
Cloning
means producing a genetically identical copy of an
individual.This is the way to be cloned. Scientists would get their DNA from a skin cell and place him in the egg of a woman whose DNA was extracted. A spark of electricitydivide the egg and, after a few days, we would obtain an embryo alike.
Much has been said in the press about human cloning. In reality, most scientists are not interested in producing human clones. What scientists want to do isproduce cloned human cells that can be used to cure some diseases.
That's how it might work, suppose you have a disease that is destroying parts of his brain slowly. Current treatments only reduce the symptoms while the diseasecontinues to damage his brain. Cloning offers hope of cure.
Scientists produce a cloned embryo using the DNA of your skin
cells. Then take stem cells from the embryo, transforming into
brain cells and then transplant them into your brain.
In contrast, an embryo in the freezer of a fertility clinic has been created from the unique mixture of sperm and egg and this is a union that only happen once,producing a totally unique set of genes that have the potential to become a unique individual.
There are several types of artificial cloning:
Molecular Cloning: is the isolation of a DNA sequence of a cell and thus
obtain copies thereof undefined. Is used in laboratories to obtain such
large quantities of a specific protein. This cloning meets with four
stages, fragmentation, ligation, transfection and selection. After this,
the cloned cells are a special culture Cell cloning, that is to create a cell
population from a single cell. The process is done using the technique in
vitro.

Therapeutic cloning: used for stem cell research. Is the production of human embryos, but not with the aim of creating people, but for research on human development. Seek to prevent or cure some diseases, like cancer, Alzheimer's, among others. Today has been very important, as scientists replaced by cloned malignant cells and thus eliminate completely any kind of pathology.
Cloning of organisms: is a process of creating a genetically identical individual to another. Such cloning is applicable to plants, seeds, fruit trees, etc..
Within the cloning of organisms, is practiced in animals. The process involves removing the nucleus from an adult cell called somatic cell to an egg cell that had its nucleus removed it previously. Then the egg with the nucleus from the somatic cell is inserted into a womb. The first to approach this type of cloning was John Gurdon in 1967, who used frog cells, but their experiment was not very successful, as the frogs died before being cloned tadpoles. He later tried similar experiments with mice and other mammals, but undoubtedly the most successful was the sheep Dolly in Scotland in 1997.
Bibliography





No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario